They are often depicted as either little green men, bug-eyed creatures or terrifying monsters intent on wiping out all life on Earth.

But if aliens do exist, what might they actually look like?
MailOnline asked a number of experts what they think — both for potential extraterrestrial life within our own solar system, as well as on distant exoplanets in faraway galaxies.
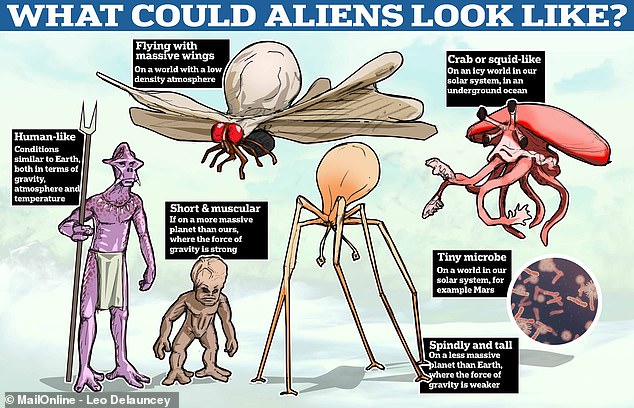
Among the wide-ranging answers were features such as big brains, enormous wings and gravity-induced spindly frames, while ‘crab or squid-like beasties’, jellyfish-esque creatures and aliens that look almost human-like are also a possibility.
The latter might seem surprising given how aliens are often portrayed in popular culture, but some experts think if another intelligent civilisation exists, life could have evolved in a similar way to us.

As one scientist put it, the reason is ‘simple physics, plus competition for food and the need to escape predation will favour organisms with similar body plans to those that are successful on Earth’.
Closer to home, if alien life does exist on Mars, Jupiter’s moon Europa or Saturn’s satellites Enceladus or Titan, it is likely to be somewhat anti-climactic because it would probably just be ‘scum-like’ microbes.
Professor David Rothery, of the Open University, said it would probably be ‘invisible to the unaided eye if you are trying to see an individual’.
He told MailOnline that it could well be ‘like a scum or a stain on the rocks of an ocean floor or a discolouration in the surface ice if there is a colony’.
That may sound a little boring, but Professor Rothery does have hope that something slightly more interesting could exist in our solar system.
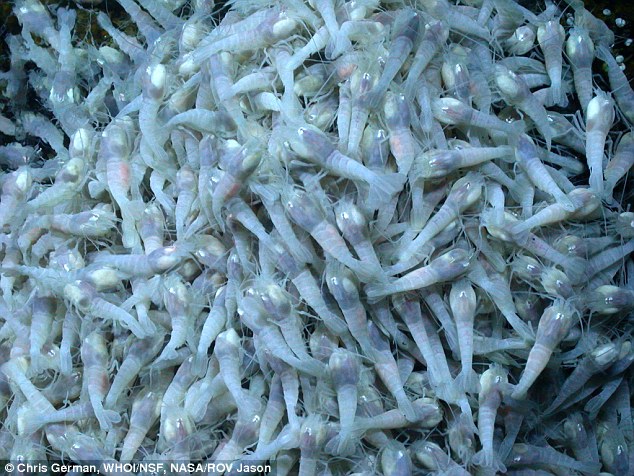
‘There may be larger organisms that have evolved to browse on the microbes,’ he said, ‘but crab-like, shrimp-like and squid-like beasties in Europa’s ocean are probably too much to hope for.’
NASA also believes that on Jupiter’s icy moon, ‘the best chance for life would be microbial’.
US space agency scientists have previously studied an ‘extreme shrimp’ ecosystem in the Caribbean to find clues about what life could be like on other planetary bodies such as Europa, which has a subsurface ocean and may have similar creatures.
Professor Andrew Coates, of University College London, thinks any life forms in our solar system would be ‘simple, single cell’.
‘But we won’t know until we find it,’ he added, ‘and the hunt is on with missions like Rosalind Franklin [the UK-built Mars rover due to launch in 2028].’
That’s near Earth though. Surely there are more mind-bending and endless possibilities in distant galaxies?
Astronomer Michael Garrett, a professor at Manchester University, thinks ‘we might be in for a shock’.
He told MailOnline: ‘I think the way complex life might appear will depend a lot on the environment within which it evolves.
‘For example, a more massive planet where the force of gravity is strong might favour life forms that are quite squat and muscular, while a less massive planet (where the force of gravity is weaker) might suit the evolution of complexities that are more delicate and potentially quite spindly and tall.’
Professor Garrett also said that if the world had a low density atmosphere, it may have ‘life forms with wings of enormous scale’.
‘Or if your star is a red giant, you might find life with eyes that are much more sensitive and larger than ours,’ he added.
‘Anyway, I’d be prepared for something very different that might be quite shocking at first but we’d hopefully soon get over that and begin to also see some similarities.’


Professor Garrett is one of a number of scientists who think human-like aliens are also a possibility.
‘Intelligent life like humans would presumably have relatively big brains, and have limbs and flexible digits that can record history and advances in knowledge that can then be passed on from one generation to the next, always building on what has gone before,’ he said.
Both Professor Rothery and Professor Simon Conway Morris, a palaeontologist at the University of Cambridge, agree that extraterrestrial life, if out there, would resemble the creatures we see around us on Earth, with limbs, heads, and bodies.
‘There is a school of thought that says that simple physics plus competition for food and the need to escape predation will favour organisms with similar body plans to those that are successful on Earth,’ Professor Rothery told MailOnline.
‘It is clearly effective to have your sense organs at the front (or top).’
He added: ‘On other Earth-like planets some have surely developed complex life forms, but its anybody’s guess what they look like.’
Professor Morris also said that any Earth-like exoplanet should evolve predators like sharks, pitcher plants, mangroves, and mushrooms, among many other things.
Another previous study suggests that in reality, aliens could be more similar to us than some would think.
The University of Oxford research indicates that life would potentially be shaped by the same processes that created humans, such as natural selection, and that these extraterrestrials may even ‘look like us’.
Lead author Sam Levin said: ‘We still can’t say whether aliens will walk on two legs or have big green eyes.
‘But we believe evolutionary theory offers a unique additional tool for trying to understand what aliens will be like, and we have shown some examples of the kinds of strong predictions we can make with it.
‘By predicting that aliens have undergone major transitions — which is how complexity has arisen in species on Earth, we can say that there is a level of predictability to evolution that would cause them to look like us.’
He added: ‘We can’t say whether or not we’re alone on Earth, but we have taken a small step forward in answering, if we’re not alone, what our neighbours are like.’
Arik Kershenbaum, author of The Zoologist’s Guide to the Galaxy, also agrees that Darwinian natural selection would apply throughout the universe.

The University of Cambridge astrobiologist said this would result in alien creatures that have symmetrical bodies with wings, legs or fins.
They would also be intelligent, have a developed language and possibly technology, he believes, and even added that humans might be able to ‘have tea with an alien’ if we came into contact with them.
Others don’t think extraterrestrial life would look like us.
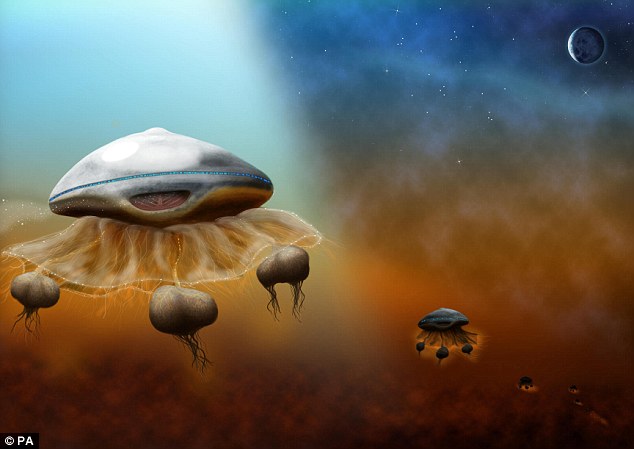
One leading space scientist previously claimed that aliens could look like giant jellyfish.
Dr Maggie Aderin-Pocock, a satellite expert and former government adviser, said extraterrestrial life was likely — but just more alien-like than some might imagine.
She believes Saturn’s moon Titan could have aliens that look like football field-sized jellyfish, complete with onion-shaped appendages and an orange underbelly or bottom.
Generated from silicon, rather than the carbon that is the basis of life as we know it, the creatures she envisions would be able to live off light absorbed through their ‘skin’ and chemicals sucked in through their giant mouths.